Introduction
Connect Buildkite to GitHub with secure, short-lived tokens.
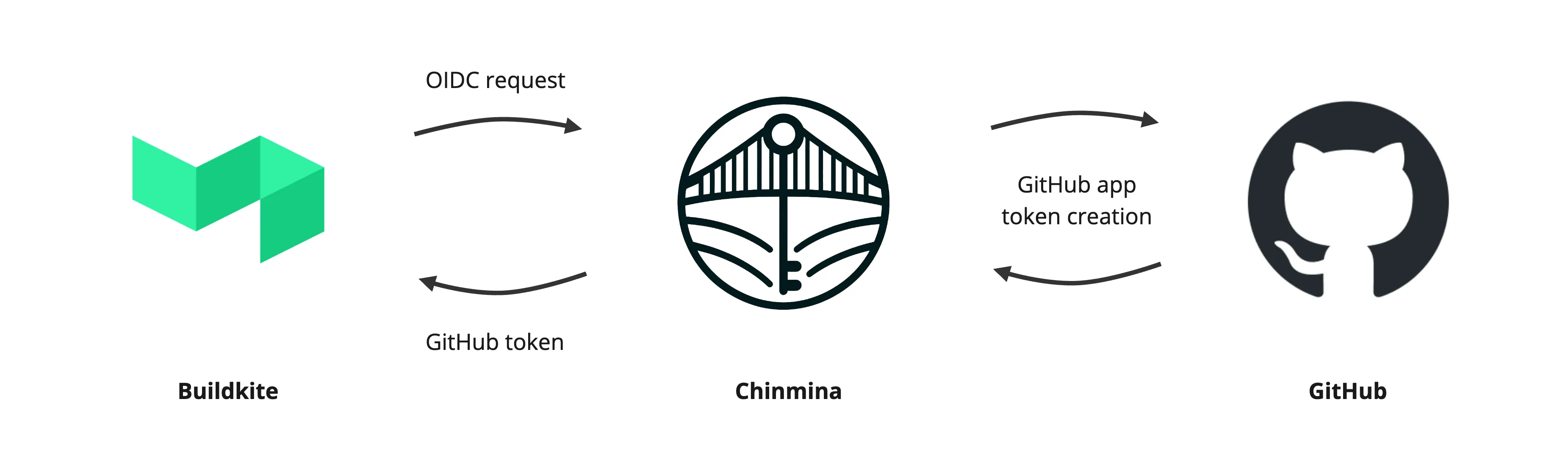
Chinmina Bridge is a simple web service that acts as an intermediary between a Buildkite installation and a related GitHub App. Buildkite agents can request ephemeral GitHub access tokens from Chinmina Bridge, removing the need to store Deploy Keys or Personal Access Tokens long term.
Benefits
Section titled “Benefits”Chinmina Bridge offers substantial security and flexibility benefits for any size organization, and scales easily as the size of your Buildkite stack grows.
Zero PATs, zero deploy keys, central permissions declarations, strong auditing and a simple runtime model make Chinmina Bridge ideal for scaling Buildkite deployments from a handful to hundreds of repositories.
Security
Section titled “Security”-
Access tokens for the repository have a lifetime of one hour and only provide read access to the pipeline repository (by default). There is no token to store and refresh: it’s entirely automatic.
-
Tokens with wider permissions can be supplied using profiles, with the same lifetime and protections as the default access tokens.
-
Issuing deploy keys per repository is no longer required. Deploy keys are long-lived credentials that require elevated repository permissions, and keys issued to individuals have a higher potential to be accidentally leaked.
-
The GitHub app private key is the only key that is stored: no other token storage is required in secrets or S3, and nothing to manage per-repository in GitHub.
-
With KMS, the highly sensitive private key cannot be extracted. When configured as described in our guide, the Chinmina service uses KMS to sign the GitHub JWT, and never has access to the raw key material.
-
Audit-friendly logs are written for each token request, whether successful or unsuccessful. These can be readily connected to your SIEM system, adding transparency and traceability to the system.
Flexibility
Section titled “Flexibility”-
Pipelines are automatically given access to the repository they’re configured for.
-
Via profiles with their flexible matching rules, additional sets of permissions can be declared centrally and accessed as required.
-
Chinmina is a straightforward Go application in a minimal container with 12-factor style configuration. It can be deployed in your choice of environment.
Considerations
Section titled “Considerations”-
Chinmina is not available as a cloud offering: it needs to be self-hosted and reachable by the Buildkite agent infrastructure.
-
It is a single point of failure in the system also, and critical to keep up. Given that it is a simple, containerized HTTP service with Open Telemetry support and easy scaling, this is thankfully relatively straightforward.
-
The private key for the GitHub application is extremely powerful, and needs to be carefully protected. It has the superset of permissions that it can delegate. Storing the key in AWS KMS and using careful resource and IAM policies on access is therefore strongly recommended.
-
Adequate controls are required on Buildkite pipeline creation. At present, the bridge will allow access by the pipeline to the configured repository. Controls are required to ensure that repository access is appropriately limited.
How it works
Section titled “How it works”Chinmina Bridge accepts HTTP connections from Buildkite agents. GitHub tokens are requested from one of the available endpoints using Buildkite OIDC token for authorization.
GitHub tokens vended by Chinmina have a maximum lifetime of an hour. Chinmina will cache tokens internally for up to 15 minutes, so the token received by an agent will have an effective lifetime of between 45 and 60 minutes.
Pipeline-based
Section titled “Pipeline-based”This is the simplest way of working with Chinmina, where a token is retrieved for the repository linked to the pipeline that is running the current build. This is a direct replacement for the deploy key or PAT that would be required instead.
Requests to /token and /git-credentials are authorized with the Buildkite
OIDC token, whose claims identify the executing pipeline. From
the pipeline, the associated GitHub repository is looked up, and a token with
contents:read permission is returned for that repository. All tokens also include
metadata:read by default.
Profiles
Section titled “Profiles”Profiles extend Chinmina’s capabilities beyond basic pipeline repository access.
Pipeline profiles allow pipelines to request elevated permissions (such as
writing pull request comments or publishing releases) for their own repository.
Pipeline profiles use the /token/{profile} and /git-credentials/{profile}
routes.
Organization profiles allow pipelines to access repositories other than
their own, useful for shared resources like private Buildkite plugins or
Homebrew taps. Organization profiles use the /organization/token/{profile} and
/organization/git-credentials/{profile} routes.
Both profile types can optionally restrict access to specific pipelines via claim matching.
Endpoints
Section titled “Endpoints”Seven endpoints are exposed:
/tokenand/token/{profile}, which return a token and its expiry for pipeline repositories/organization/token/{profile}, which returns a token and its expiry for organization profiles/git-credentialsand/git-credentials/{profile}, which return the token and repository metadata in the Git Credentials format for pipeline repositories/organization/git-credentials/{profile}, which returns the token and repository metadata in the Git Credentials format for organization profiles/healthcheck, which returns 200. It is used for healthcheck requests from load balancers and the like.
